Ergonomic Considerations for Desk and Chair Height: Correct Desk And Chair Height
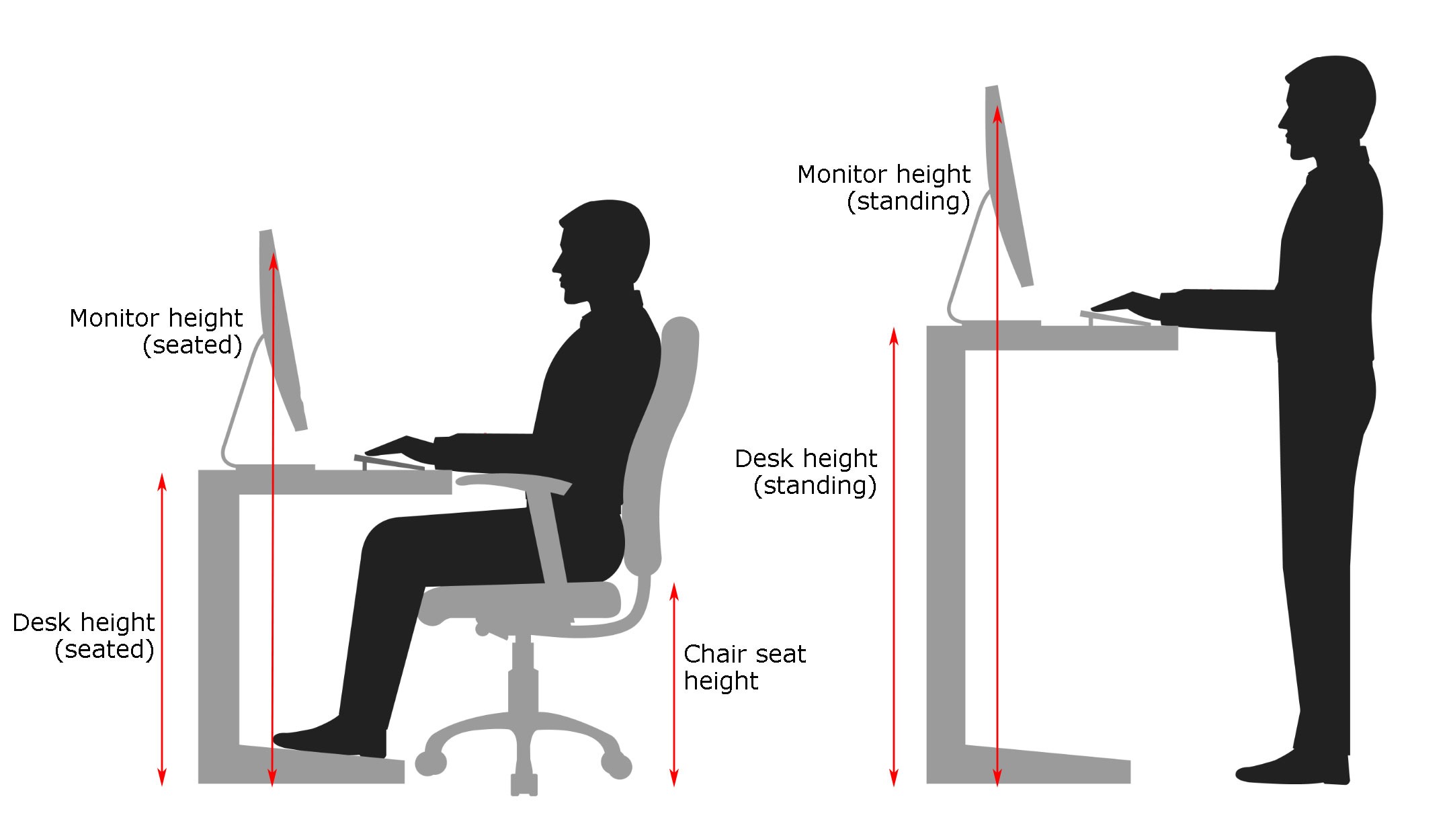
Proper desk and chair height is crucial for maintaining good posture and preventing long-term health problems. Ignoring ergonomic principles can lead to discomfort, pain, and even serious musculoskeletal issues. This section will explore the impact of incorrect setup, guide you through measuring ideal heights, and offer practical tips for optimal comfort and productivity.
Impact of Incorrect Desk and Chair Height on Posture and Long-Term Health
Incorrect desk and chair height significantly impacts posture. Sitting too low forces you to hunch over, straining your neck, shoulders, and back. Conversely, sitting too high causes you to reach for your keyboard and mouse, leading to similar strain and potential carpal tunnel syndrome. Long-term consequences can include chronic back pain, neck pain, headaches, and repetitive strain injuries. These issues can reduce productivity, impact overall well-being, and even necessitate expensive medical interventions. Maintaining a neutral spine, where the natural curves of your back are supported, is paramount. This minimizes stress on your joints and muscles.
Measuring Ideal Desk and Chair Height, Correct desk and chair height
Determining the ideal desk and chair height is a personalized process. It involves considering your individual body measurements. First, measure your forearm length from your elbow to the ground while standing. Your desk height should ideally be at elbow height, allowing your forearms to rest comfortably on the desk surface. For your chair, the seat height should allow your feet to be flat on the floor, with your thighs parallel to the ground. Your knees should be at a 90-degree angle or slightly higher. Adjusting your chair’s lumbar support to maintain the natural curve of your lower back is also essential. If your feet don’t reach the floor, use a footrest to maintain proper posture. Remember, these are guidelines; fine-tuning is necessary to find your perfect ergonomic setup.
Practical Tips for Adjusting Desk and Chair Height
Start with the chair: Ensure your feet are flat on the floor, and adjust the seat height accordingly. Next, adjust your desk height so your elbows are at approximately 90 degrees when typing. If using a monitor, position it at eye level to avoid neck strain. Consider using a keyboard tray for optimal wrist positioning, preventing strain. Regularly check your posture throughout the day and make minor adjustments as needed. Take short breaks to stand and stretch to counteract prolonged sitting. A standing desk converter can be a useful tool to incorporate more standing into your workday. Invest in a chair with adjustable features like lumbar support and armrests. These adjustments are critical for sustained comfort and productivity.
Comparison of Adjustable vs. Fixed Height Desks and Chairs
| Feature | Adjustable Height Desk | Fixed Height Desk | Adjustable Height Chair | Fixed Height Chair |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ergonomic Benefits | Supports various postures and heights, reducing strain. | Limited ergonomic adaptability, may not suit all users. | Allows for personalized seating adjustments, improving posture. | May not be suitable for all users; can lead to discomfort. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive. | Less expensive initially. | Moderately priced; varies based on features. | Least expensive option. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; adapts to user needs and preferences. | Low flexibility; limited adjustment options. | Good flexibility; accommodates individual needs. | Limited flexibility; adjustments are often minimal or absent. |
| Long-Term Health Impact | Reduces risk of musculoskeletal disorders; promotes better health. | Increases risk of posture-related problems over time. | Minimizes discomfort and risk of long-term issues. | Higher risk of developing posture problems and back pain. |
